A Practical Look At Data Governance In The Life Sciences
By Jennifer Lee, CEO and founder, JLC Advisory, LLC

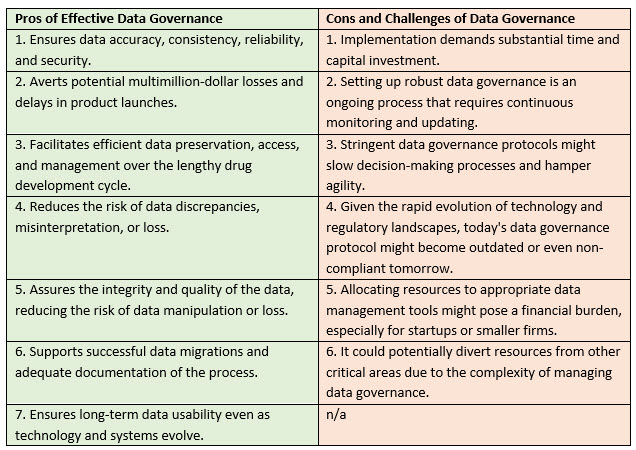
Data gaps pose significant challenges for businesses. They can impede product development and result in multimillion-dollar losses and delays in product launches. These concerns are amplified in the life sciences industry, where the journey from research to market-ready, lifesaving products can span a decade if not more. A great deal can occur in this amount of time.
Consider Company A, which was established several decades ago with a laboratory prototype that has the potential to revolutionize cancer treatments. The company was finally ready to submit a new drug application (NDA) following failed tests, external changes, and executive mismanagement. However, it reencountered difficulties with data packages. The gaps in these data packages from decades of research and clinical trials impeded the company's commercialization efforts.
Similarly, Company B encountered a significant data gap from numerous previous non-clinical laboratory studies. The Premarket Approval (PMA) application was delayed for over a year, and several hundreds of millions of dollars were spent to address the problems.
A few examples of data gaps illustrate the typical difficulties life sciences face regarding data accuracy, consistency, and accessibility. Troubleshooting, data cleanup, and revalidation can add months to a schedule that is already tight. Variations in data collection methods, coding standards, or terminology across a program can also complicate data gaps. In addition, the long-term preservation of data in different systems and databases over 10 to 15 years impedes data accessibility and utilization, compounding the previously mentioned challenges.
Without solid data governance, there is an increased risk of data discrepancies, misinterpretation, or even loss, which can hamper the development process and, ultimately, delay the delivery of treatments to the market. Therefore, a well-structured and robust data governance strategy is beneficial and imperative for organizations in the life sciences industry.
The question arises, what exactly is data governance? It is an organization-wide data management system that seeks to ensure data accuracy, consistency, dependability, and security. This system encompasses multiple factors, including data quality, integrity, management policies, standards, privacy, security, and compliance. This aspect of data quality focuses on the data's accuracy, completeness, and consistency.
Hurdles And Considerations
As technology progresses rapidly, systems and software used for data creation and storage risk becoming outdated. After two decades, present systems may cease to exist, emphasizing the need to ensure continued data accessibility and usability. Data governance offers a framework for preserving data and ensuring its longevity, thus facilitating your company’s ongoing access to and utilization of critical data throughout the drug development life cycle.
Another complication is the migration of data across different systems over time. Several migrations might occur over 10 to 15 years, necessitating the verification of successful migrations and a comprehensive understanding of the reasons and results. Data governance aids in addressing these concerns by establishing clear data management policies, standards, and protocols. This ensures smooth data migrations and promotes adequate documentation and comprehension of the process.
Although establishing effective data governance protocols is ideal, it has its hurdles and implications. First, implementing these protocols can demand a substantial investment of time and capital. This could represent a substantial financial burden for many organizations, especially startups or smaller firms in the life sciences industry. This is due to the costs of necessary technology infrastructure, software solutions, and professional expertise to guide the process.
Second, setting up robust data governance is not a one-time effort but rather an ongoing process. It requires continuous staff monitoring, updating, and training, adding to operating costs and possibly diverting resources from other critical areas.
Third, there's the risk of hampering agility. Stringent data governance protocols might slow decision-making processes, as compliance checks and validation protocols could become time-consuming. This may impede a company's ability to react swiftly to new opportunities or threats.
Lastly, given the rapid evolution of technology and regulatory landscapes, the data governance protocol that seems effective today might become outdated or even non-compliant tomorrow. Thus, an overemphasis on establishing perfect data governance today might leave a company less prepared to adapt to future changes.
5 Strategies For Long-term Success
- Establish comprehensive data management protocols.
- Formulate and establish specific data management policies and procedures, including data collection, validation, storage, and analysis. All team members must understand and commit to these policies and procedures.
- Ensure consistency through regular data quality checks.
- Conduct routine data quality checks to identify any inconsistencies or errors. These discrepancies must be investigated and resolved immediately.
- Invest in future-proof data management technology solutions.
- Allocate resources to appropriate data management software and tools to ensure efficient data storage, management, and analysis. Verify that these solutions adhere to regulatory requirements and best practices in the industry.
- Continually evaluate and optimize data management practices.
- Regularly evaluate and modify data management practices to ensure their relevance and efficacy.
- Maintain detailed data logs for transparency and traceability. Keep thorough records of all data and its sources and any changes or improvements made to the data over time.
- Integrate stakeholder feedback for continuous improvement. To enhance data management practices, incorporate feedback from stakeholders, team members, and regulatory agencies.
- Prioritize data security and privacy measures, including access controls, encryption, and backups, to protect data from unauthorized access, breaches, or loss.
In conclusion, even though data governance in the life sciences industry presents unique challenges and implications, its benefits significantly outweigh potential drawbacks. It provides a vital foundation for data accuracy, consistency, dependability, and security, all indispensable attributes for successfully developing and launching life-saving treatments. It is impossible to overstate the significance of a robust and adaptable data governance strategy as we progress further into the data-driven future.
About The Author:
 Jennifer Lee is the CEO and founder of JLC Advisory, LLC, a life sciences consulting firm. She has held positions in small, mid-sized, and large pharma/biotech companies and is an expert in advancing drug development pipelines from preclinical to commercialization. She has overseen the development of product candidates in oncology, CNS, infectious/rare disease, and immuno-gene/cell therapies. She contributed to the global approval of seven novel therapies and has also contributed to licensing agreements, successful exits, and improved labels. Lee graduated from the University of Illinois at Chicago with a bachelor's degree in biochemistry and from Northwestern University with a master's degree in clinical research and regulatory administration.
Jennifer Lee is the CEO and founder of JLC Advisory, LLC, a life sciences consulting firm. She has held positions in small, mid-sized, and large pharma/biotech companies and is an expert in advancing drug development pipelines from preclinical to commercialization. She has overseen the development of product candidates in oncology, CNS, infectious/rare disease, and immuno-gene/cell therapies. She contributed to the global approval of seven novel therapies and has also contributed to licensing agreements, successful exits, and improved labels. Lee graduated from the University of Illinois at Chicago with a bachelor's degree in biochemistry and from Northwestern University with a master's degree in clinical research and regulatory administration.
